Organic solar cells have the advantages of light weight, flexibility, low cost, and low light response, and are currently the hot research directions of solar cell technology. High-efficiency, flex-resistant, and inexpensive flexible organic solar cells have strong potential for application in flexible wearable and portable electronic devices, photovoltaic building integration, and military applications. At present, the research results of most organic solar cells are based on rigid tin oxide (ITO) glass substrates. However, if organic solar cells are to be commercialized, their real advantage is to use low-cost wet printing and roll-to-roll large-area processes. In organic solar cells, the most commonly used electrode material is indium-doped tin oxide (ITO). However, ITO has problems such as poor electrical conductivity and mechanical fragility on plastic substrates, and ITO is usually processed by vacuum sputtering at a high temperature, which makes it expensive and unfavorable for preparation using large-area printing and roll-to-roll. There have been some reports that new electrode materials have been used in place of conventional ITO, such as nanosilver wires, graphene, carbon nanotubes, conductive polymers, etc., among which poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):poly(styrene) The cost of the sulfonic acid) (PEDOT:PSS) film is relatively low, and the film exhibits high optical and electrical properties, excellent thermal stability, good flexibility, and the like. The use of acid doped PEDOT:PSS can greatly increase its conductivity, but most of the current reports use strong acids such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, etc. Doping, and then high-temperature post-processing, easy to damage the PET and other flexible plastic substrates.
Recently, Ge Ziyi, a researcher at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, based on the previous research on high-efficiency organic solar cells (Nature Photonics, 2015, 9, 520; Advanced Materials, 2018, 30, 1703005; Macromolecules, 2018, DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00683; Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6, 464), made new progress in the field of flexible organic solar cells, and innovatively developed low temperature acid treatment PEDOT:PSS electrode replacement requires high temperature sputtering and Expensive ITO electrode. The low-temperature methanesulfonic acid treatment improves the conductivity of the PEDOT:PSS film and reduces the roughness of the film, while avoiding the destruction of the flexible plastic substrate by the conventional strong acid treatment. Further, by using the all-solution processing technology and using PBDB-T and IT-M non-fullerene active layers, a single-junction flexible organic solar cell with non-ITO processing in a wet process was prepared, and the energy conversion efficiency of the battery reached 10.12%. The highest efficiency of the fully wet-processed flexible organic solar cells reported. Moreover, this type of fully solution-processed flexible organic solar cell is very suitable for the technical requirements of large-area preparation processes such as roll-to-roll printing and blade coating, and provides an important reference path for the low-cost and flexible preparation of organic solar cells. The work was published in the international journal Advanced Materials under the title All Solution-Processed Metal Oxide-Free Flexible Organic Solar Cells with Over 10% Efficiency. Ge Ziyi and team member Fan Xiwei are the co-authors of the paper, and master student Song Wei is the first author.
The above research has obtained the national key R&D plans (2017YFE0106000 and 2016YFB0401000), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51773212, 21574144 and 21674123), the Chinese Academy of Sciences Frontier Science Key Research Project (QYZDB-SSW-SYS030), the Chinese Academy of Sciences Key International Cooperation Project (174433KYSB20160065), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Cross-innovation team, Zhejiang Outstanding Youth Fund (LR16B040002) and Ningbo Science and Technology Innovation Team (2015B11002, 2016B10005) and other funding.
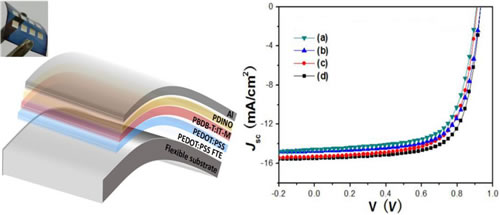
Figure: Schematic diagram and photovoltaic characteristics of flexible organic solar cells
An electric actuator is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It is used to control the movement of various mechanical systems, such as valves, dampers, and other industrial equipment. Electric actuators are commonly used in industrial applications where precise positioning, speed control, and high accuracy are required. They are also used in the automotive industry, aerospace industry, and medical equipment. Electric actuators are available in different types, including linear actuators, rotary actuators, and multi-axis actuators. They can be powered by AC or DC power sources and can be controlled by various types of controllers, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs).
Electric Actuator,Electric Linear Actuator,Electro Hydraulic Actuator,Electric Actuator Valve
WUXI KVC-VALVE , https://www.kvgatevalve.com