0 preface
Reactive dyes are the most commonly used dyes for cotton dyeing, and their batch dyeing methods are still the most popular for cotton knitwear) JnT method. Among the reactive dyes, the green-green, bright blue and black-based cyanine dyes still use a single-reactive vinylsulfone-type reactive dye, and the double-reactive dye is a commonly used type.
In order to develop a dye formulation with a constant color, that is, reproducible and streamlined, various dye manufacturers recommend different color matching prescriptions for light, medium and dark colors. Dyeing workers can use two or three different dye prescriptions from the same manufacturer to dye different colors. These dyes are not necessarily a single dye, but may be a special mixed dye to obtain a dyed product with high exhaustion rate and good reproducibility.
It is well known that post-dyeing is an important part of reactive dyeing to achieve the desired fastness properties. According to relevant statistics, the processing time of cotton knitwear after dyeing accounts for 30% to 35% of the whole dyeing process, including rinsing one and one water washing, soaping, rinsing, washing and fixing. In order to meet the end user's fastness performance requirements, the dyed product should be completely free of unfixed hydrolysis dyes, but this may require additional soaping/rinsing/washing, which not only increases process time, but also increases The water consumption.
Nowadays, due to the scarcity of water resources, it is actually not feasible to increase the treatment process of water washing, and this process also has the disadvantage of increasing the amount of sewage. In order to obtain the required wet fastness and optimize the use of water resources, usually, after one or two high-temperature soaping, the dye fixing agent is used to "fix" the unwashed hydrolyzed dye without affecting the wet fastness evaluation. . In addition, post-treatment with a cationic dye fixing agent prevents contamination problems caused by the hydrolyzed dye in an unsuitable storage environment.
Cationic dye fixing agents for reactive dyes are now considered to be eco-friendly products. They are not based on formal and have different chemical properties than formals. However, the performance of each dye fixing agent varies depending on the formulation. The main problem with dye fixing agents is that the dyed product undergoes a change in color and shade upon treatment. Although the dye fixing agent supplier promises that the product has little effect on the color, the color shade of the dyed product after fixing is still difficult to predict.
Researchers at Sarex in India have studied this to explore the correlation between the chemical properties of dye fixing agents and the change in shade. In this preliminary study, the researchers performed color depth staining in the dark and medium colors. Dark colors include navy, purple sauce, dark green, and medium colors are gray, olive, and brown. The effect of dyeing products on color shade after treatment with four different chemical types of dye fixing agents was studied.
1 test method
1.1 fabric
The scoured, bleached 100% cotton single jersey fabric, the fabric sampled from the production was washed again in the laboratory and neutralized to a pH of 6.5.
1.2 dye
SumifixHF, RemazolRR, RemazolRGB are used for dyeing dark dyes; SumifixE-XF, CibacronFN, LevailxCA are used for dyeing medium dyes. All dye samples are supplied by dye manufacturers for laboratory research testing. Although the colors dyed with different series of dyes do not exactly match in the shade, the color depths visually observed in the dyes are kept as similar as possible in the test to investigate the effect of the dye fixative on the shade.
1.3 dyeing
Dyeing was performed on a laboratory dyeing cup dyeing machine at a bath ratio of 1:10, dyed according to standard techniques recommended by the dye manufacturer.
1.4 soap cooking process
After fixing with alkali, it was rinsed with running water for 5 min, with a rolling liquid in the middle, neutralized with acetic acid to pH 6, and washed with water at this pH value and temperature 95 for 10 min. It was rinsed with reflowed water for 5 min and boiled with 2% Kalium NNS and 2% Sarakol PS at temperature 98 for 10 min. Add a soap to the dark color, use flowing water at the temperature
95 rinse for 10 min, neutralize to pH 6. The rinse and soaping water was soft water with a pH of 6.5, and the bath ratio was maintained at 1:10. The soaping efficiency has been demonstrated by previous tests to ensure that the hydrolyzed dye is completely removed prior to treatment with the dye fixing agent.
1.5 dye fixing agent treatment
Four dye fixing agents were used, the dosage was 1% (owf), the bath ratio was 1:10, and the pH value was 6,40. The rolling mill liquid maintains a uniform moisture content, 100 is dried and the moisture content is checked.
1.6 color rating
The DA and DB values ​​were assessed using a colorimetric computer and the CIELAB equation and compared to unfixed dyes.
1.7 dye fixing agent
Fixing agent 1#: SuperfixAMGNConc. Dicyandiamide formal product; fixing agent 2#: SarafixNF504 epichlorohydrin polyamine polycondensate; fixing agent 3#: Sarafix. AP polyethylene polyamine polycondensate; fixing agent 4#: Sarafix. WP special formula, ultra-low formaldehyde, stable under temperature 70 washing fastness test (AATCC61.3A).
2 results and discussion
The test results are shown in Tables 1 to 6.
2.1 The effect of fixing agent on the color shade of dark green dyed products
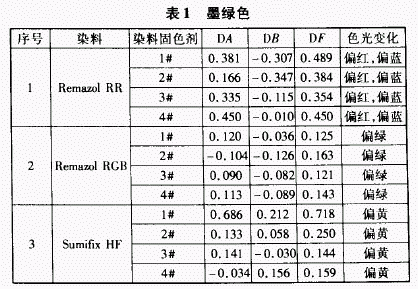
When the dark green color was dyed with RemazolRR, the color change after treatment with Fixing Agent 1# was the largest, and the change of Fixing Agent 4# was the smallest. The four fixing agents make the color of the treated dyes reddish and bluish, but the degree of change is different. When color matching with RemazolRGB, the color difference is much smaller than RemazolRR, but the color is greenish. When color matching with SumifixHF, Fixing Agent 1# has the largest change in color light compared with the other three fixing agents. Compared with RemazolRR and RemazolRGB, the dye has a yellowish hue, that is, lacks blue light.
2.2 The effect of fixing agent on the color shade of purple sauce coloring products
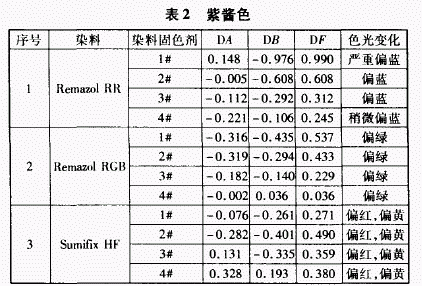
When using RemazolRR color matching purple sauce color, the color light is mainly blue, among which, the fixing agent 1# is the most serious, the fixing agent 2#, 3# is the second, the fixing agent 4# is the smallest; when the color is changed by RemazolRGB, the color difference is changed. It is much smaller than RemazolRR, but the shade is greenish. Among them, the fixing agent 1# and the fixing agent 2# have an effect on the color light
Large, and fixing agent 4# has the lowest effect on color light; when color matching with SumifixHF, fixing agent 4# has the greatest influence on color light, compared with ReinazolRR and RemazolRGB dye, the color is reddish and yellowish, and the other three are solid.
The toner also has similar results.
2.3 The effect of fixing agent on the color of the dyed products
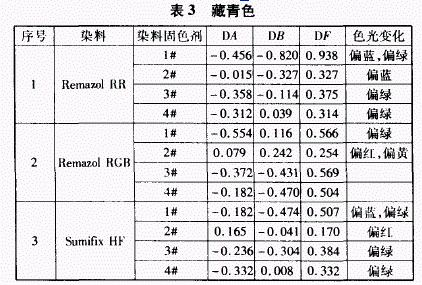
When using Remazol I / I / color matching navy, Fixing Agent 1 # has the greatest influence on the color light, and its color becomes blue and green. The other three fixing agents have similar results, but the degree of color tone changes. Fixing agents 3# and 4# make the color light green, while fixing agent 2# makes the color light more blue
When using RemazolRGB color matching, Fixing Agent 1# makes the color light greener, so the color of the dyed product looks a little yellowish; and the effect of Fixing Agent 2# on the shade of the dyed product is completely deficient with the RR dye, and the color shift is partial. Red and yellowish! The effects of the fixing agents 3# and 4# on the shade have more or less similar results.
When color matching with SumifixHF, the fixing agent 1# makes the color light blue and greenish, and the fixing agent 3# makes the color greenish, but the degree of bluishness is light. Fixing agent 4# makes the color light more green. Very differently, Fixing Agent 2# makes the color reddish! The effect on the color light is very different from the results of the other three fixing agents.
2.4 The effect of fixing agent on the color of brown dyed products
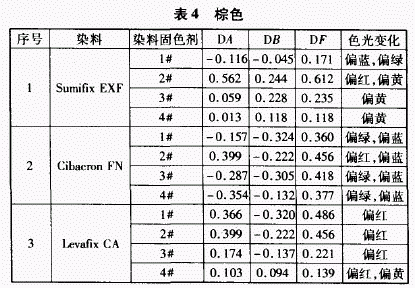
When the SumifixEXF dye is used, the fixing agent 2# makes the color reddish yellowish and the color light changes the most. Fixing agents 3# and 4# make the color shade yellow, while the DA value does not change much, and the fixing agent 1# makes the color light slightly blue and green, and the effect of the other three fixing agents on the color light different.
When the Cibacron FN dye was used, the fixing agent 2# made the color reddish, while the other three fixing agents made the color greenish. All dye fixing agents make the color shade blue, the highest DB value is Fixing Agent 1#, and the lowest is Fixing Agent 4#.
When using the LevafixCA dye, the four dye fixing agents make the shaded red. Among them, Fixing Agent 4# has the least influence on the color light, and it is the only fixing agent which makes the dyed product slightly yellowish.
2.5 Fixing effect of color fixing agent on olive dyeing
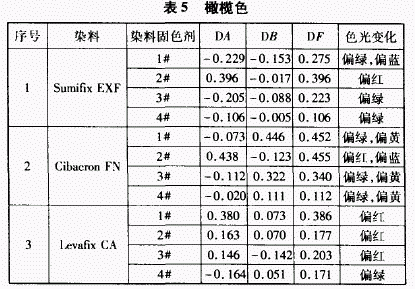
When the SumitqxEXF dye is used, the fixing agent 2# makes the color reddish, and after the other three fixing agents, the color light is greenish. Except for Fixing Agent 1#, the other three fixing agents have little effect on the DB value. Compared with the other three fixing agents, after the fixing agent 1# treatment, the color shade is blue.
For the Cibacron FN dye, Fixing Agent 2# reddens the shade, while the other three fixatives give the shade a little greenish. Fixing agents 1#, 3# and 4# make the color yellow, while only the fixing agent 2# makes the color blue.
When coloring with the LevafixCA dye, except for the fixing agent 4#, the other three fixing agents make the color reddish, and only the fixing agent 4# makes the color greenish. Except for the fixing agent 3#, the DB values ​​of the other three fixing agents were substantially unchanged.
2.6 Fixing effect of fixing agent on gray dyeing
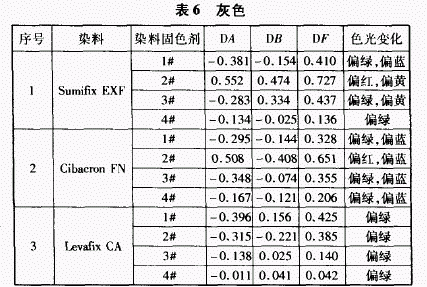
When the SumifixEXF dye is used, in addition to the fixing agent 2#, the color light is polarized to the infrared, and the other three fixing agents make the color light greenish. Further, the fixing agents 2# and 3# cause the color to be yellowish, and the fixing agents 1# to 13 make the color light blue. The DB value of the fixing agent 4# did not substantially change.
When using the Cibacron FN dye, similar to the Sumitlx EXF dye, the Fixing Agent 2# also causes the shade to be reddish, while the other three fixatives cause the shade to be greenish. The four fixing agents here make the color blue. The DB value of the fixing agent 3# has the smallest change. For the LevafixCA series of gray color matching dyes, except for the fixing agent 4#, which has no effect on the color light, the other three fixing agents make the color light greenish.

3 Conclusion
For the medium color, the fixing agent 4# has the lowest DF value. This means that Fixing Agent 4# has the least effect on shade, which is very important for colors such as olive, gray and brown. But for dark colors, this conclusion is not reached.
For the color matching of various dyes of the medium color, the fixing agent 2# makes the color light reddish. Through experiments, it can be concluded that for medium and dark colors, formaldehyde-free dye fixing agents are superior to dicyandiamide formal products, and have little effect on color light. Based on the above studies, dyeing workers can use the appropriate dye fixing agent to adjust the final product.
In order to prevent the color change caused by the dye fixing agent after dyeing, the dyeing worker can build a database of various dye prescriptions and study the effects of various types of dye fixing agents on the color light. .
Custom Tape Measure,Rubber Measuring Tape,Carpenter Tape Measure,Craftsman Tape Measure
HENAN SHIJI HUALIAN TOOLS AND MEASURE CO.,LTD , https://www.hnsjhl.com