The application of nitrogen fertilizer should be based on urea and ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride and ammonium hydrogencarbonate cannot be applied. Because ammonium sulfate is a physiological acid fertilizer, when applied in a large amount, ammonium sulfate will be dissociated into ammonia and sulfate in soil moisture, and ammonia will be absorbed by melon, leaving sulfate and hydration to synthesize sulfuric acid, which will acidify the soil. , affecting the production of vegetables in the future. In addition to accelerating soil acidification and compaction, chlorine chloride is harmful to cucumber and must be strictly prohibited. Ammonium bicarbonate is a weak acid and weak base salt, which is very unstable. Especially the greenhouse cucumber grows in a closed high temperature environment. After the ammonium bicarbonate is applied to the soil, it will decompose and produce ammonia quickly. When the melon is not fully absorbed in time, it is redundant. The ammonia will be gasified into the shed. When the ammonia gas encounters the water droplets on the leaf surface, ammonia water is formed, and the lower leaves are yellowed. In severe cases, the green leaves are necrotic, which seriously affects the yield and even the harvest.
Diammonium phosphate is mainly a phosphate fertilizer, and also contains a certain amount of nitrogen (about 17%), but the phosphorus of diammonium phosphate is poorly moved into the soil, and it is difficult to move with water in the ditch, so the effect of topdressing is not good. In order to improve the application effect, it is necessary to first soak the diammonium phosphate in water for 24 hours, and then use the leachate to topdress, which is more troublesome. Of course, if this contradiction is solved by combining the underground automatic infiltration irrigation and topdressing, it can directly deliver the available phosphorus dissolved in the water to the root soil for absorption and utilization of the melon, which is an ideal method of topdressing. Potassium sulphate in potash can be used as top dressing, but it should not be applied more to prevent soil acidification. Superphosphate is a phosphate fertilizer, and it is not suitable for top dressing due to poor mobility of available phosphorus. Potassium dihydrogen phosphate is a quick-acting phosphorus-potassium compound fertilizer with good solubility and can be used as top dressing. Potassium chloride cannot be used as a top dressing.
The number of top dressing should be based on the principle of less and diligent, that is, the amount of topdressing can not be more than each time, generally it is appropriate to chase 40-50g per ridge (30 strains). If you feel that the amount of fertilizer is insufficient, you can increase the number of top dressings. This will not cause fat damage, but also ensure high yield.
It is strictly forbidden to plant the cucumber in the shed, and it is strictly forbidden to dry and apply the ditch. It must be applied with the ditch. In the high-yield period, every water should be fattened and the high-yield period should be extended.
Foliar topdressing is a cost-effective method of topdressing. Generally, in the middle and late stages of production, it is found that the leaves are thin and yellow when the nitrogen fertilizer is applied. The urea is 50g to 15kg of water. After fully stirring and dissolving, the leaves are sprayed, every 5-7d1 times, for 3-5 times, which can receive very good. effect. When it is found that the melon is serious, the melon leaves are hypertrophy, and the deformed melon is more, the potassium leaf dihydrogen phosphate 50g is stirred and dissolved in 15kg of water and sprayed on the leaf surface, 3-5d1 times, and can also receive certain effects. In the later stage of production, the roots are senescent, and 50g of water and 15kg of potassium dihydrogen phosphate can be used at the same time. Then, half a bottle of sprayed Shibao is added, and the leaves are sprayed after being dissolved. There is a substitute for root dressing, which increases disease resistance and delays aging. The role of high yield in the later period. It should be noted here that under normal circumstances, pesticides for disease prevention and treatment cannot be added to the fertilizer at the same time, otherwise it is not a phytotoxicity or a drug failure. When it is necessary to spray at the same time, it should also be sprayed in the morning and sprayed in the afternoon to prevent phytotoxicity.
About the various types of compound fertilizers, mixed fertilizers, organic fertilizers, flush fertilizers and various foliar fertilizers that appear on the market today, it is best to use them after comparative tests.
Germanium Plano-Convex (PCX) Lenses feature precision diamond turned surfaces making them ideal for a variety of infrared applications, including thermal imaging, infrared spectroscopy, and remote sensing. Germanium (Ge) is popular for its high index of refraction, broad transmission range, and rugged mechanical properties. These lenses are available in 25 and 50mm diameters, uncoated, or with multiple broadband coating options.
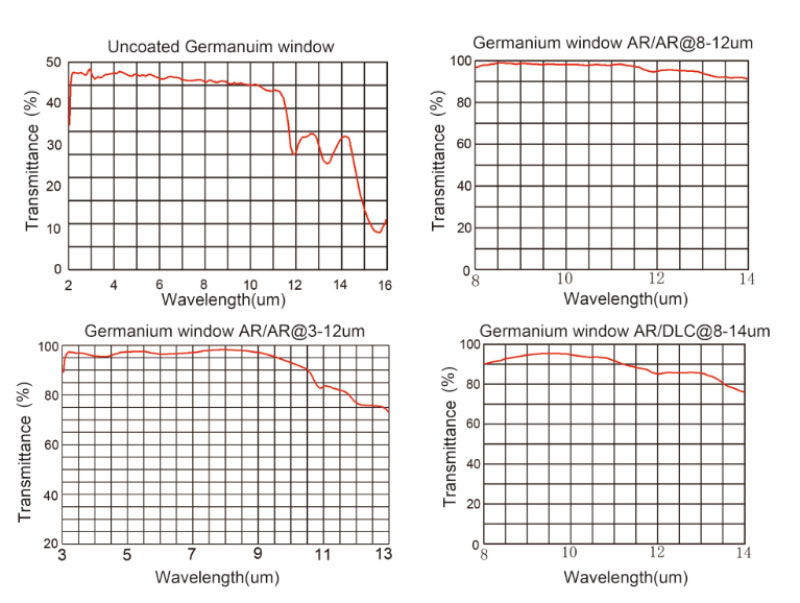
Germanium (Ge) material feature high index of refraction (around 4.0 from 2 - 14μm), an anti-reflection coating is recommended on these germanium windows for sufficient transmission in the region of interest. Germanium is subject to thermal runaway, meaning that the transmission decreases as temperature increases. As such, these germanium windows should be used at temperatures below 100°C. Germanium`s high density (5.33 g/cm3) should be considered when designing for weight-sensitive systems. 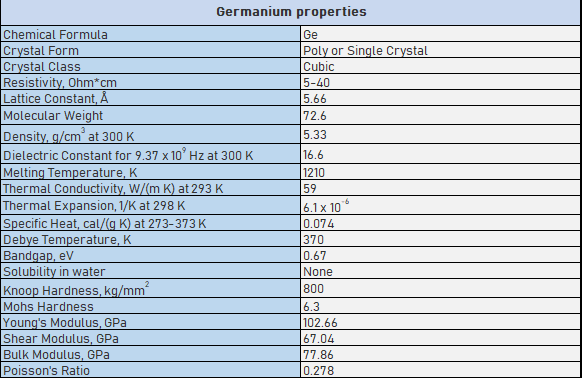
|
Germanium windows specifications |
||
| Standard precision | High-precision | |
| Dimension Tolerance | φ5-250mm+0/-0.2 | φ3-350mm+0/-0.2 |
| Thickness Tolerance | 1-50mm+/-0.1 | 1-50mm |
| Parallelism | 1 arc minute | 10 arc seconds |
| Surface Quality | 60/40 | 20/10 |
| Flatness | N<λ/2@633nm(at 50mm) | N<λ/10@633nm(at 50mm) |
| Clear Aperture | >90% | >95% |
| Chamfer | Protected <0.5mmx45deg | Protected <0.5mmx45deg |
Germanium Lens,Ge Infrared Aspheric Lens,Germanium Aspheric Lens,Germanium Infrared Lens
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.realpoooptics.com